Fresh Vegetable Product Processing Guide
Release time:
2025-01-06 20:25
Fresh-Cut Vegetable Processing Line: A Step-by-Step Guide
Fresh processed vegetables are an essential part of daily diet, eat plenty of fresh, quality vegetables every day. The vegetables preparation requires hygienic, stable quality and efficient equipment to ensure freshness and extend shelf life. This article explains the key steps involved in processing fresh-cut vegetables using a professional vegetable processing line.
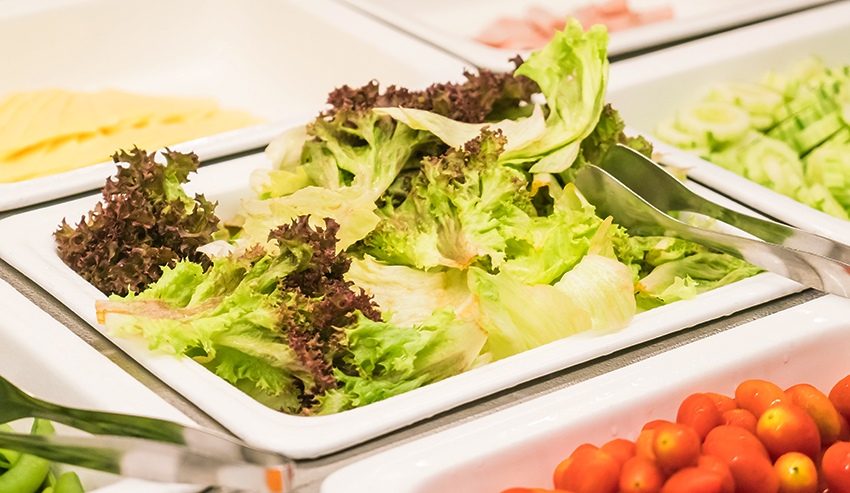

Steps in Fresh-Cut Vegetable Processing
Sorting and Grading
Vegetables are soaked in a water tank for manual sorting and grading. Workers separate them based on size and quality while removing debris, yellow leaves, and damaged parts. Soaking time should not exceed 30 minutes.
Cleaning
Thorough cleaning is crucial for maintaining freshness. It reduces bacteria and washes off residues that could cause spoilage, removes impurities and dirt. Can be cleaned by air bubbles or ultrasonic washing, followed by a water spray to rinse thoroughly.
Cutting
Proper cutting ensures the vegetables look good and stay fresh longer. Small cuts increase surface area and reduce shelf life, so cutting should be minimized. Use sharp blades for cleaner cuts to avoid bruising and discoloration.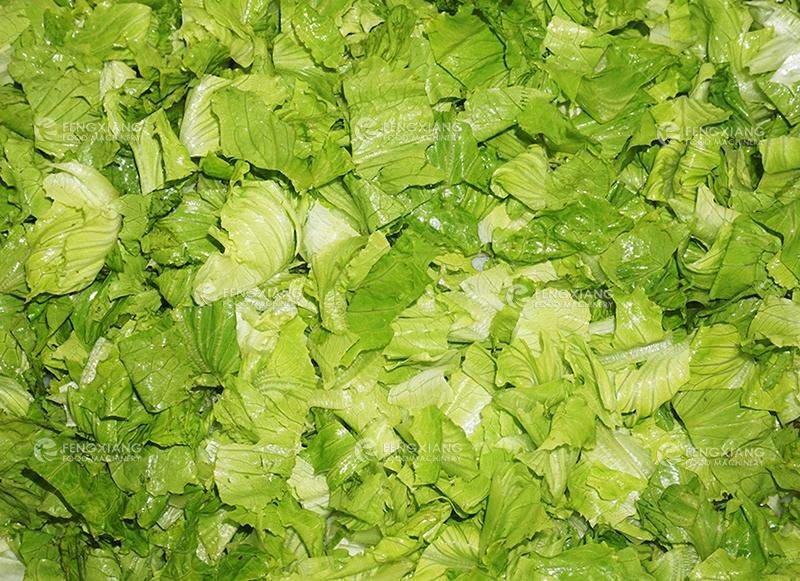
Preservation
Cutted vegetables are easy to spoilage due to mechanical damage. Preservation treatments, such as soaking in solutions with ascorbic acid, citric acid, or sodium bisulfite, can prevent browning and extend freshness. Adjust soaking times and concentrations to balance effectiveness and flavor.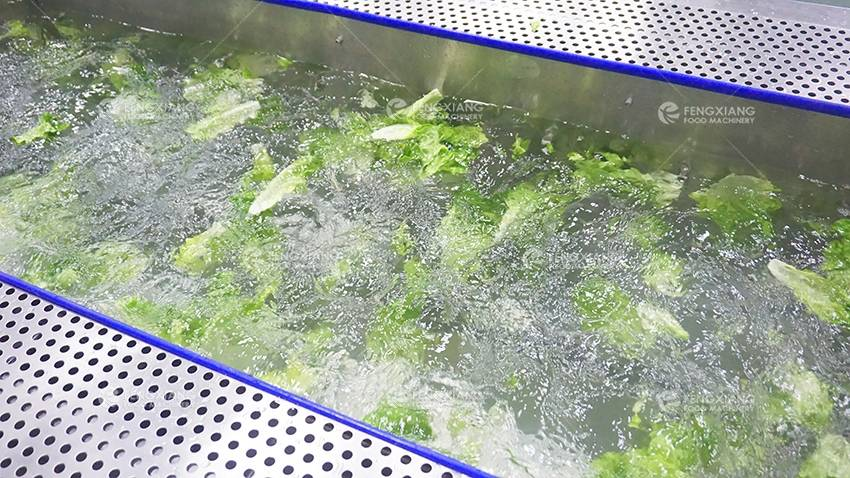
Dehydration
After preservation, excess moisture is removed to maintain quality. A centrifuge is commonly used for efficient dehydration. Centrifugal dehydration can preserve the appearance of vegetables as much as possible.
Sterilization
Sterilization eliminates remaining bacteria on the vegetables. A UV sterilizer is often used for this purpose. The duration of sterilization should be controlled to avoid overheating and maintain vegetable quality.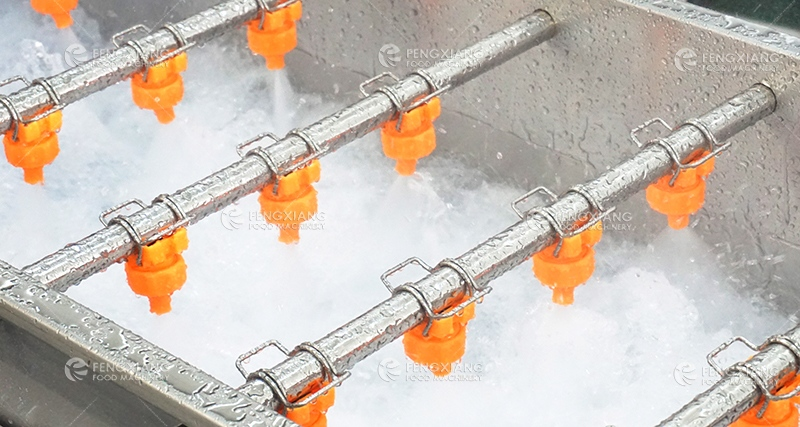
Packaging
Packaging is critical to protecting fresh-cut vegetables. Vacuum packaging is commonly used for its cost-effectiveness, while MAP (Modified Atmosphere Packaging) provides better preservation but at a higher cost.
Cold Storage
Low temperatures slow down the vegetables' respiration and nutrient loss. Store fresh cutted vegetables at 4°C–8°C to maintain quality without causing cold damage. This helps extend shelf life and ensure freshness.
A well-designed fresh-cut vegetable processing line integrates sorting, cleaning, cutting, preservation, dehydration, sterilization, packaging, and cold storage. Each step is crucial for ensuring high-quality, safe, and long-lasting fresh-cut products.
Next
Related cases
Complete Guide to Industrial Pineapple Processing Lines
Our complete pineapple processing line covers peeling, coring, cleaning, cutting, and drying solutions designed for industrial production. With high yield, low waste, and modular automation, it helps manufacturers achieve consistent quality, export-level hygiene, and higher profitability.
Salad Production Line Case Verification, Automated Salad Cutting, Washing & Dewatering Solution
This case study showcases how an automated salad production line—featuring sorting, cutting, vortex washing, vibrating dewatering, and continuous dewatering—helps global customers improve efficiency, enhance food safety, and expand large-scale salad operations. Real cases from Indonesia, Saudi Arabia, and EU suppliers highlight its high processing capacity, strong customization, and significant cost-saving benefits.
Marketing Plan for Mango Peeling Machine
We provide a mango processing machine that delivers a major upgrade in global mango production. It solves low efficiency, high loss, safety risks, and inconsistent quality found in manual operations. The machine adapts to mainstream global mango varieties, handles peeling–pitting–slicing automatically, minimizes fruit loss, and maintains stable, high-precision results.